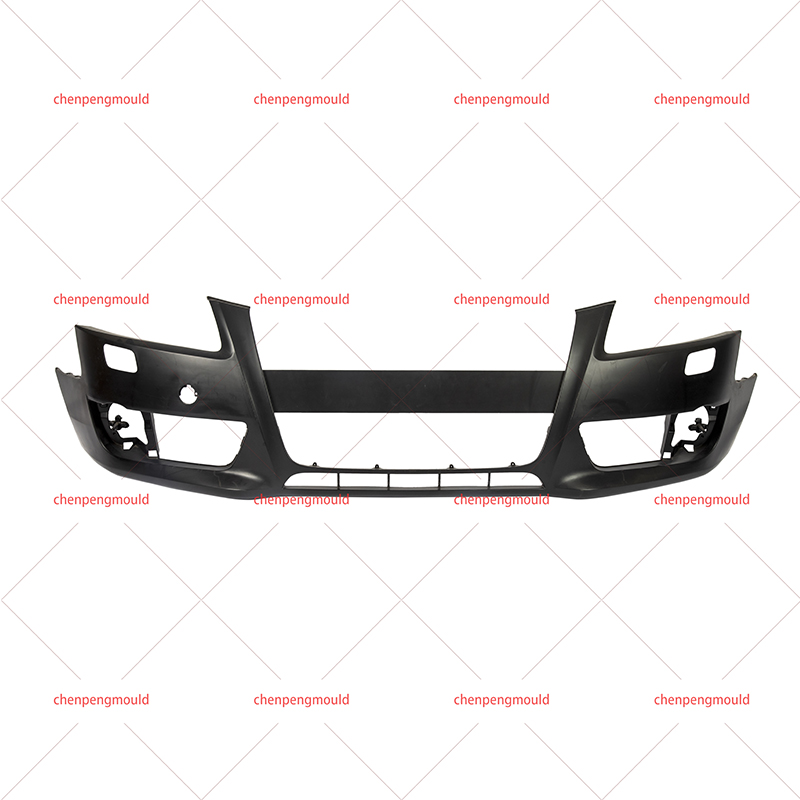
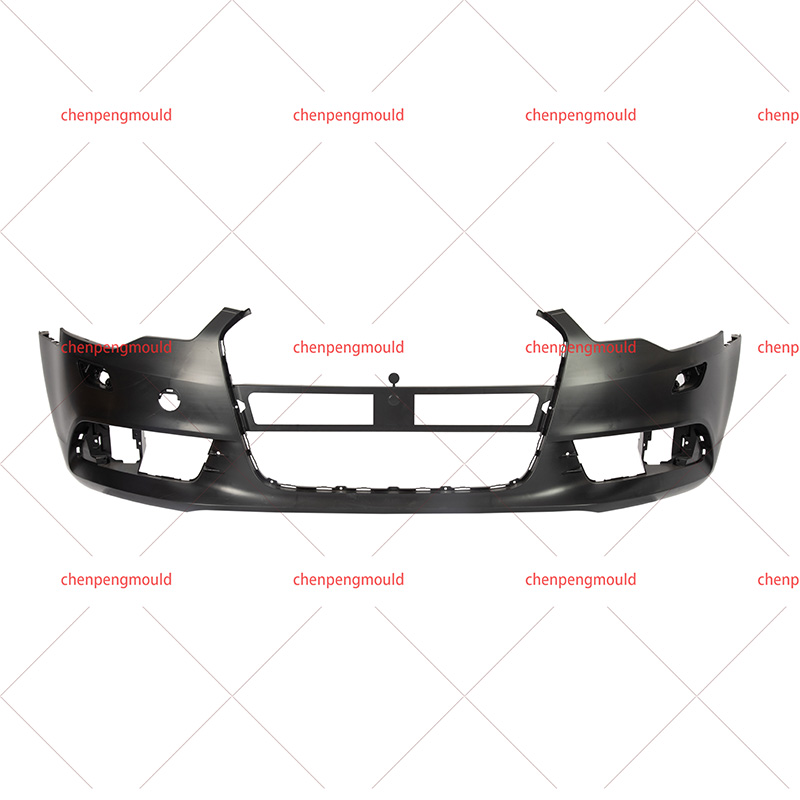
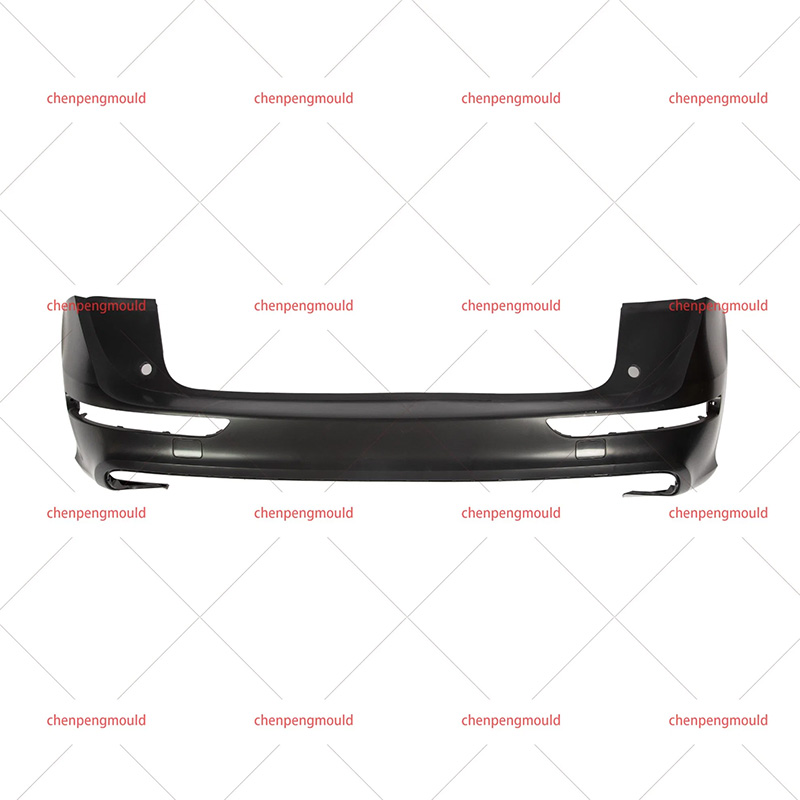
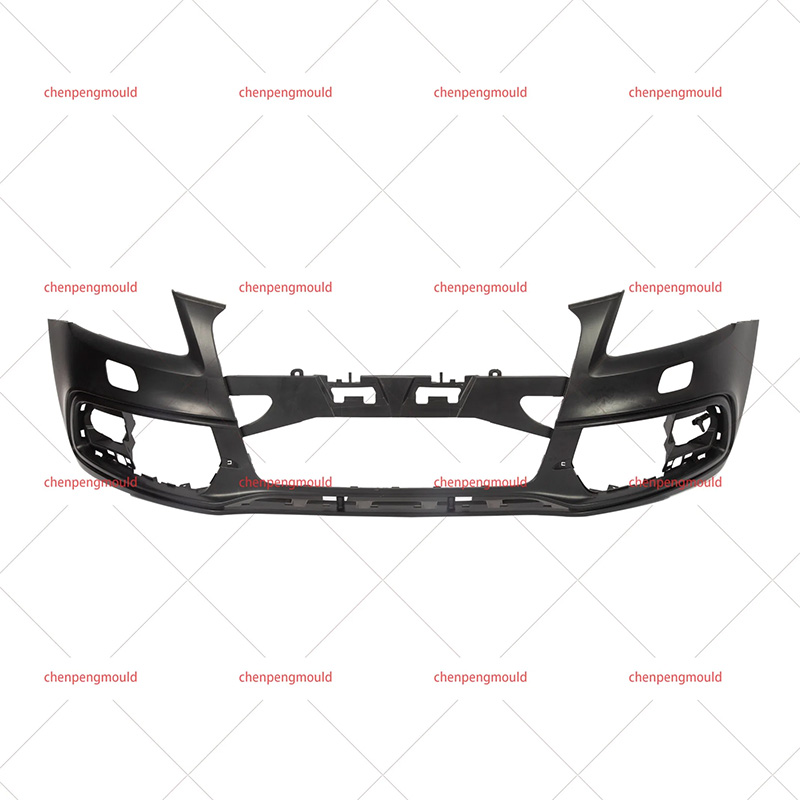
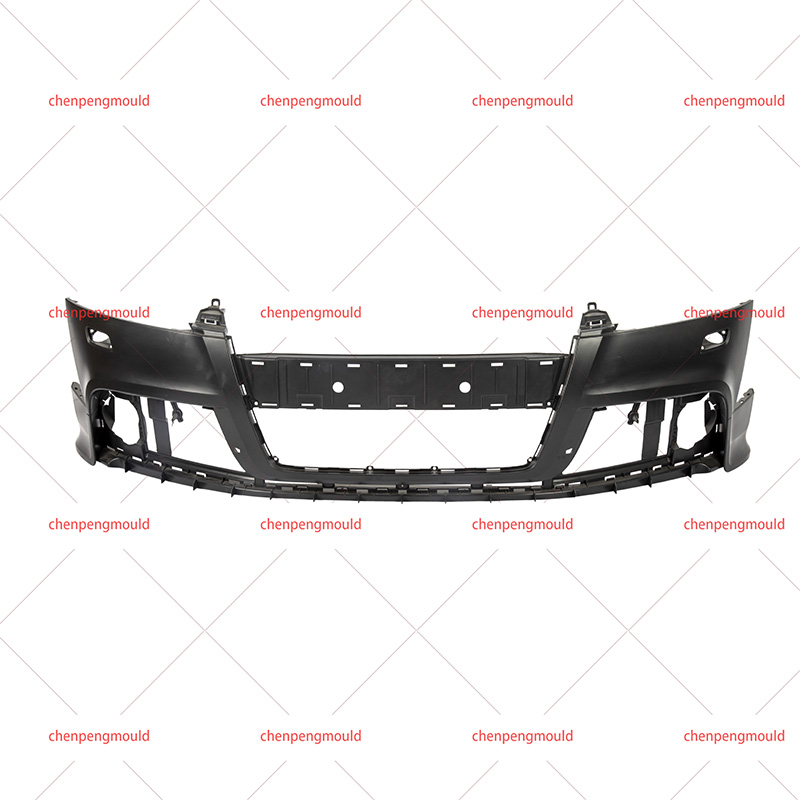
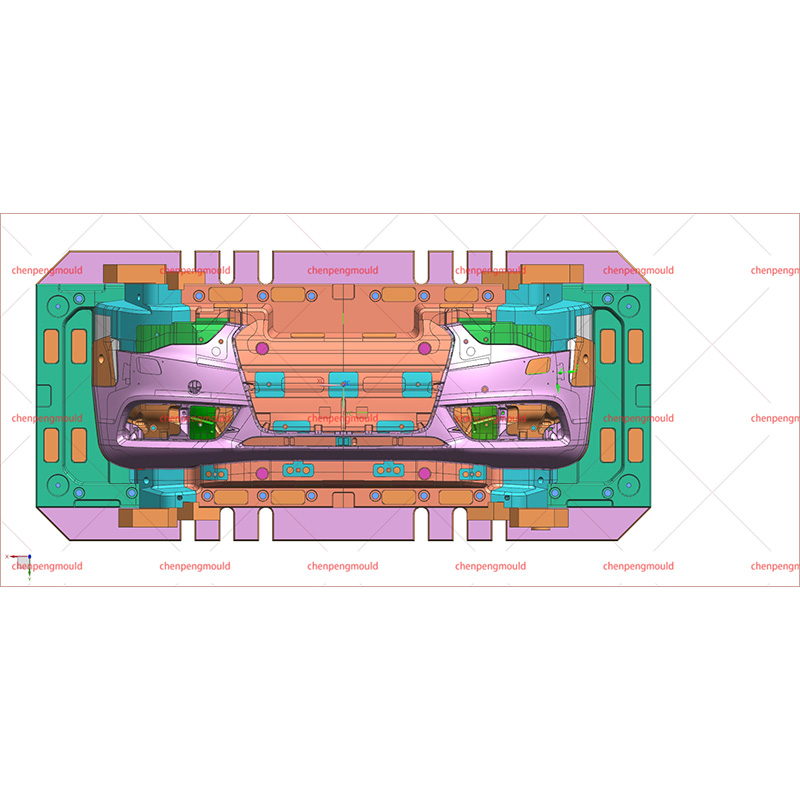
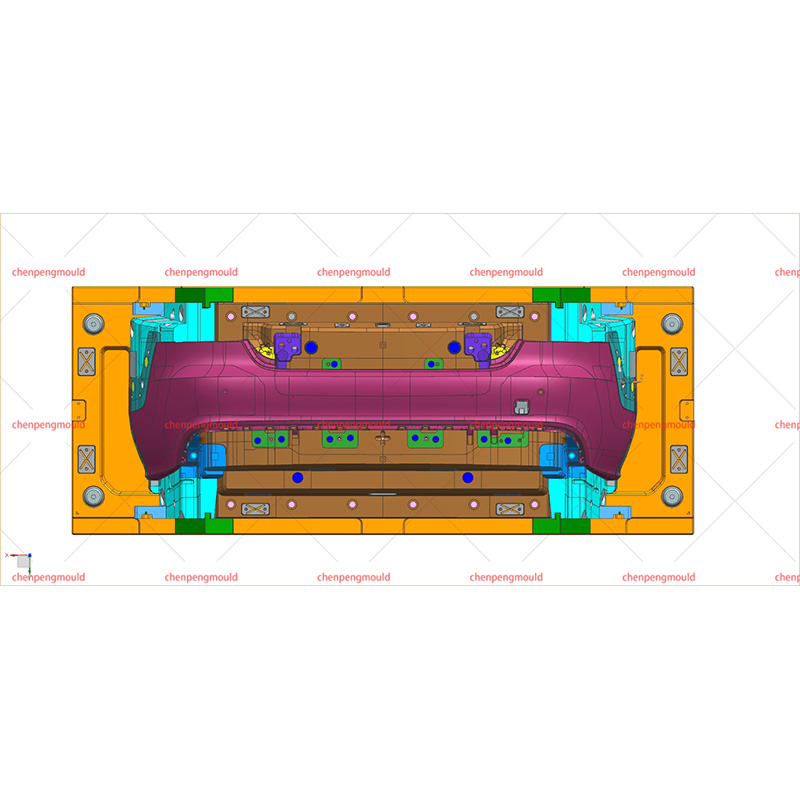
Molded automotive bumpers are essential components that significantly impact the safety and visual appeal of vehicles. Crafted from carefully chosen resins like polypropylene and ABS, these thermoplastic polymers offer a unique blend of strength, flexibility, and lightweight properties. The meticulous molding process ensures precise designs, consistent quality, and the ability to absorb impact energy during collisions.
I. The Resin Behind Molded Automotive Bumpers:
Polypropylene (PP):
Polypropylene is the most commonly used resin for molded automotive bumpers. This thermoplastic polymer boasts a winning combination of properties, including high impact resistance, excellent durability, and a lightweight nature. These characteristics make PP an ideal choice for manufacturing automotive bumpers that need to withstand various external forces.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene):
ABS is another popular resin choice for molded automotive bumpers. This thermoplastic polymer offers a good balance of toughness and rigidity. ABS bumpers are known for their impact resistance and ability to maintain their structural integrity in different weather conditions. Additionally, ABS is easily moldable, contributing to the efficient manufacturing of complex bumper designs.
II. Functions of Molded Automotive Bumpers:
Impact Absorption:
The primary function of an automotive bumper is to absorb impact during collisions or low-speed accidents. The carefully selected resin provides the necessary flexibility and strength to absorb and disperse the energy generated upon impact, minimizing damage to the vehicle and ensuring the safety of occupants.
Aesthetic Enhancement:
Beyond safety, molded automotive bumpers play a significant role in enhancing the overall aesthetics of a vehicle. Manufacturers can mold intricate designs and shapes, giving each vehicle model a distinct appearance. The ability to achieve complex designs contributes to the vehicle's visual appeal and brand identity.
Weight Reduction:
The choice of lightweight resins, such as polypropylene, contributes to the overall weight reduction of the vehicle. This not only improves fuel efficiency but also has positive implications for environmental sustainability. Lighter vehicles generally consume less fuel and produce fewer emissions.
III. Unique Characteristics of Molded Automotive Bumpers:
Molded Automotive Bumper:
The term Molded Automotive Bumper refers to the process of crafting automotive bumpers through injection molding or compression molding techniques. This precise manufacturing process allows for the production of bumpers with consistent quality, high accuracy, and intricate details. The molded automotive bumper sets the standard for modern vehicle design and manufacturing.
The Automotive Resin Bumper Mold refers to the tooling used in the molding process. These molds are meticulously designed to shape the chosen resin into the desired bumper form. The quality and precision of the mold directly influence the final product's appearance, structural integrity, and performance.
In conclusion, molded automotive bumpers, crafted from resins like polypropylene and ABS, play a pivotal role in ensuring both the safety and aesthetic appeal of vehicles. The unique combination of impact absorption, lightweight design, and intricate molding processes makes these bumpers indispensable in the automotive industry. As technology and materials continue to advance, the evolution of molded automotive bumpers will likely contribute to safer, more visually appealing, and environmentally friendly vehicles on our roads.
Molded automotive bumpers, born from the fusion of advanced resins and intricate molding processes, embody a perfect synergy of safety, aesthetics, and efficiency in the automotive industry. The careful selection of resins like polypropylene and ABS ensures resilience and impact absorption, while the precise molding techniques allow for the creation of visually appealing and structurally sound components. As vehicles evolve, molded automotive bumpers continue to be at the forefront, contributing to both the safety of occupants and the distinctive design elements that define modern automobiles.




 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666