China Sale Bumper Injection Mold Supplier Manufacturer
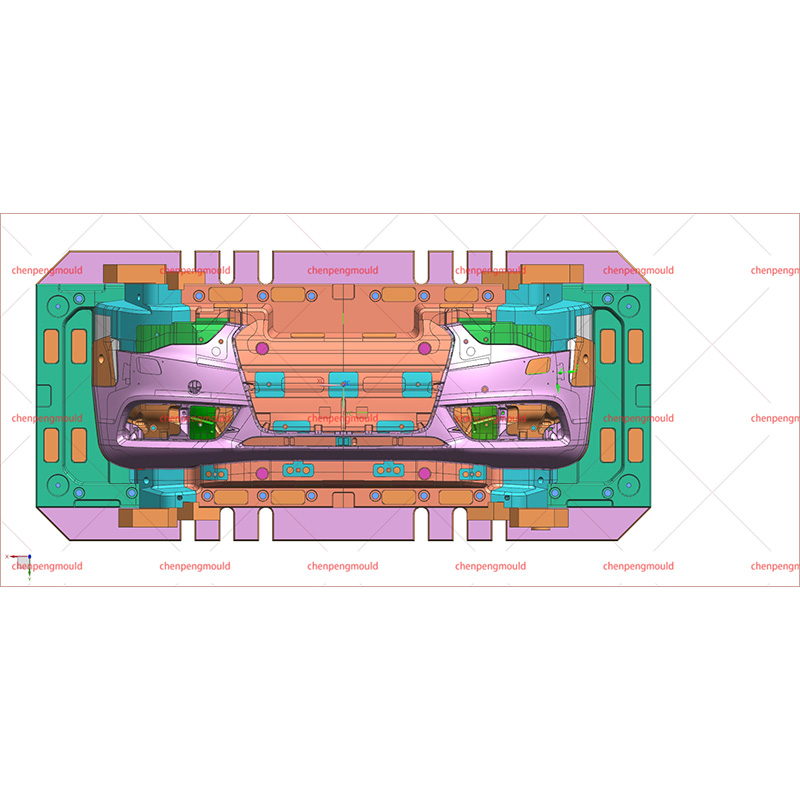
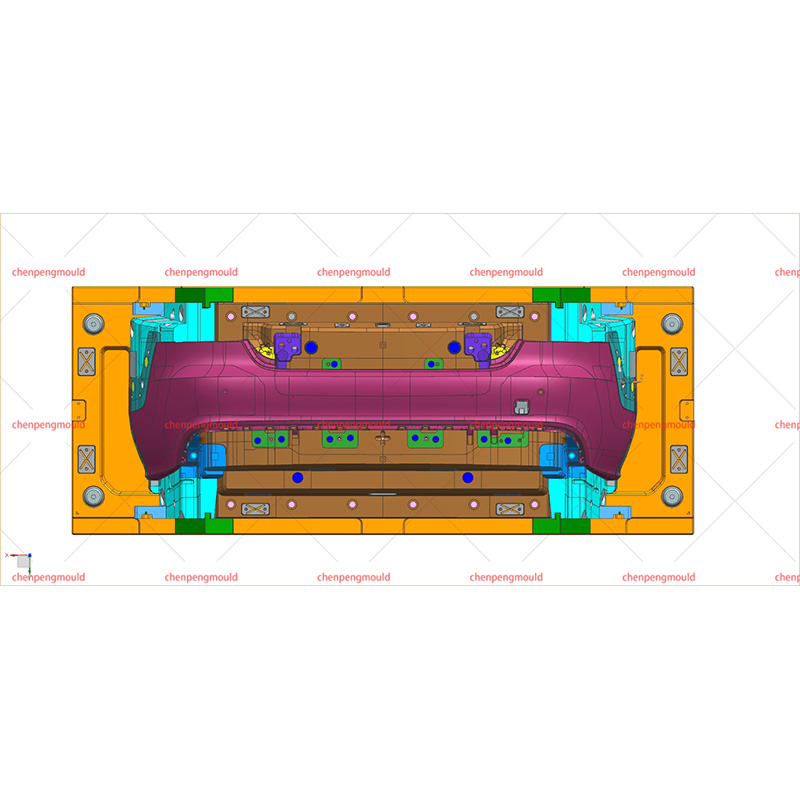
The design of a bumper mold is a critical aspect of the automotive manufacturing process. Bumpers serve not only as aesthetic features but also as essential components for vehicle safety and performance. The design and manufacturing of bumper molds require careful consideration of materials, design techniques, and production methods to ensure quality, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Before diving into mold design, it’s important to understand the primary functions of a bumper. Bumpers are designed to absorb impact during minor collisions, protecting both the vehicle’s structure and its occupants. They also contribute to the vehicle's aerodynamics and aesthetics. Given these multifunctional roles, the design of the bumper and its mold must ensure that the finished product can withstand various stresses and impacts.
Material Selection
The choice of material is one of the crucial aspects of bumper mold design. Common materials include:
Polypropylene (PP): Widely used for its balance of strength, flexibility, and cost. It is lightweight and can be easily molded into complex shapes.
Polyurethane (PU): Known for its durability and impact resistance, polyurethane is often chosen for applications requiring enhanced energy absorption.
Thermoplastic Olefins (TPO): These materials combine the benefits of plastic and rubber, offering flexibility and resistance to environmental factors.
Each material comes with its own set of advantages and limitations. Therefore, the choice often depends on the specific performance requirements of the bumper, production costs, and the desired aesthetic qualities.
Design Considerations
The design of the bumper mold itself involves several key factors:
Complex Geometry: Bumpers often feature intricate designs that require precise molds. Designers must ensure that the mold can accommodate these shapes without compromising the structural integrity of the final product.
Draft Angles: To facilitate the easy removal of the molded bumper from the mold, incorporating appropriate draft angles is essential. Insufficient draft can bring about difficulties in demolding, which can damage the part or the mold itself.
Ventilation: Proper ventilation in the mold design is crucial to avoid defects such as air traps or burn marks on the molded part. Strategically placed vents can allow air to escape during the injection process, ensuring a smooth flow of material.
Cooling Systems: Effective cooling is vital to reduce cycle times and ensure consistent quality. Designers should integrate cooling channels within the mold to maintain temperatures during the injection process.
Mold Material: The selection of materials for the mold itself can influence the production process. Common choices include steel and aluminum, each offering different durability and cost-effectiveness. Steel molds are generally more durable but also more expensive, while aluminum molds are lighter and easier to work with but may not withstand high production volumes.
Prototyping and Testing
Before moving to full-scale production, creating prototypes is an essential step in the design process. Prototyping allows designers to evaluate the mold’s performance and make necessary adjustments. Rapid prototyping techniques, such as 3D printing, can be used to create physical models quickly and economically. Testing these prototypes under real-world conditions helps identify any potential weaknesses in the design and ensures that the bumper will perform as intended.
Manufacturing Techniques
Once the design has been finalized, the manufacturing process begins. The common technique for producing bumper molds is injection molding. This process involves injecting molten material into the mold under high pressure, allowing for quick production of complex shapes. Factors influencing the injection molding process include temperature, pressure, and cycle time, all of which must be carefully monitored to achieve high-quality results.




 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666