Automotive Plastic Injection Molding Mould Custom Company
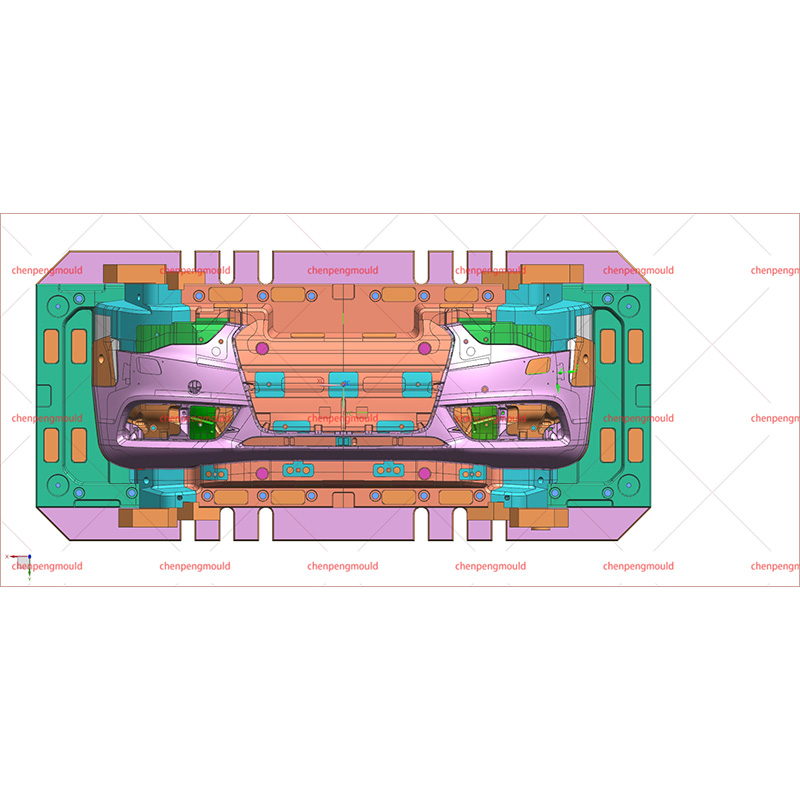
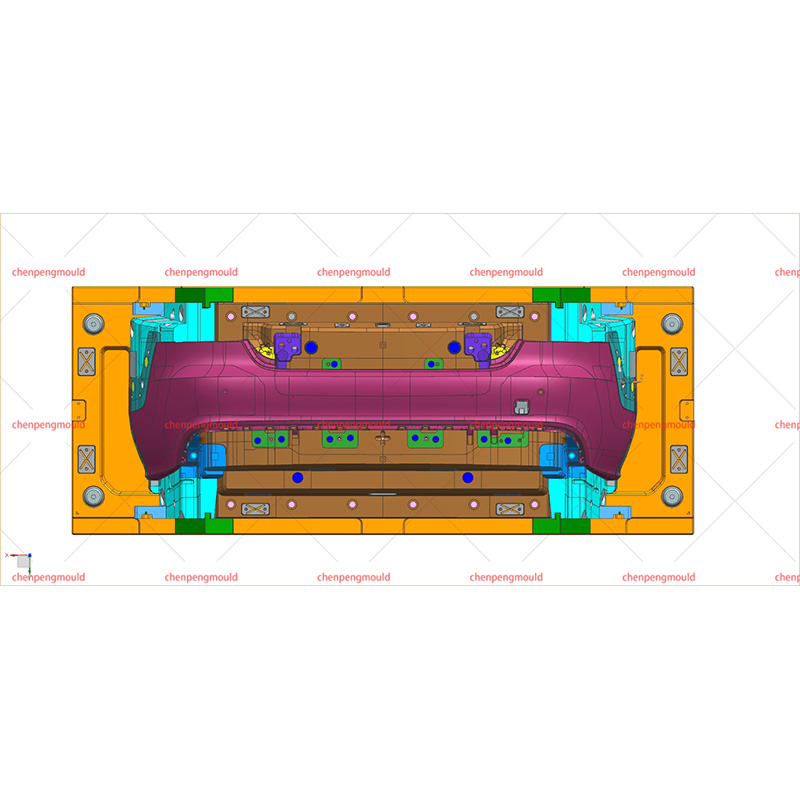
In the realm of automotive design, few elements are as critical as the automotive mould. This seemingly inconspicuous component plays a crucial role in shaping the various parts of a vehicle, influencing both its functionality and aesthetic appeal. Understanding the intricacies of automotive moulding reveals much about the precision and artistry involved in modern vehicle design.
One of the primary functions of automotive mould is to ensure precision and consistency in vehicle parts. Moulds are designed to create parts with exact dimensions and surface finishes, which is crucial for maintaining the quality and safety of the vehicle. Consistency in moulding ensures that each part produced meets stringent standards, contributing to the overall reliability and performance of the vehicle.
Automotive moulds enable designers to explore new ideas and innovate. With advanced moulding techniques, manufacturers can create custom parts that enhance both the functionality and aesthetics of the vehicle. For example, complex shapes and intricate designs can be achieved through the use of advanced automotive moulding technologies, allowing for greater creativity and customization in vehicle design.
The use of automotive moulds contributes to cost efficiency in manufacturing. By enabling high-volume production of parts with minimal waste, moulding processes help reduce production costs. This efficiency is particularly important in the automotive industry, where economies of scale play a significant role in keeping vehicle prices competitive.
Types of Automotive Moulding Processes
1. Injection Moulding
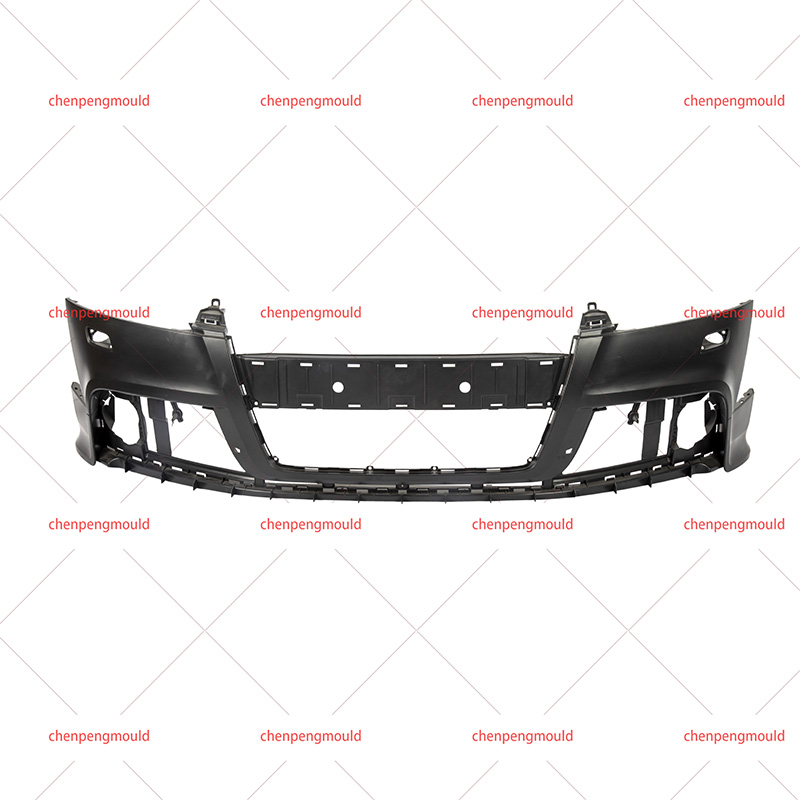
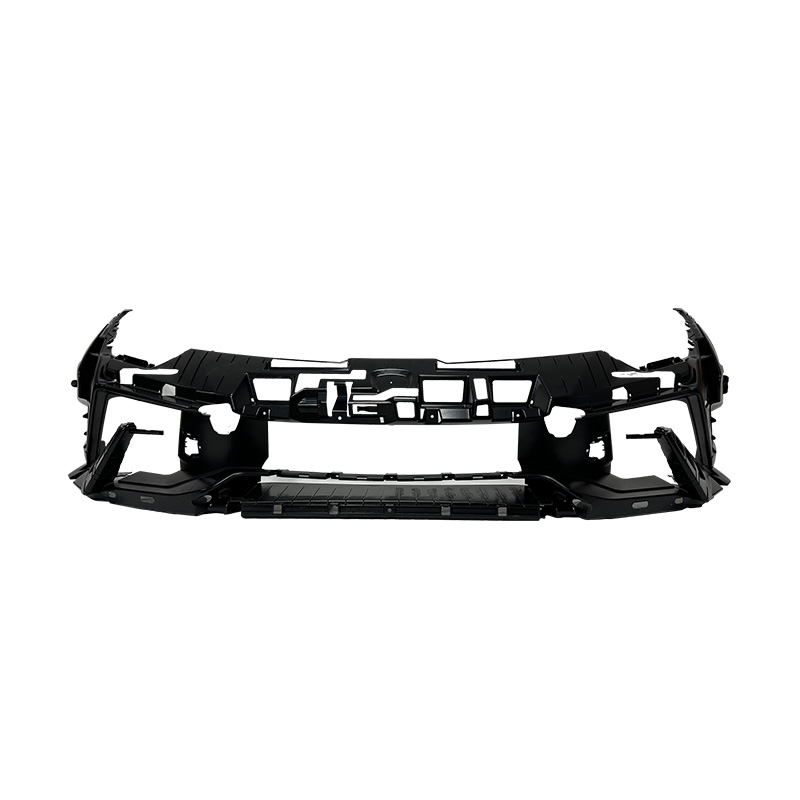
Injection moulding is one of the common methods used in automotive moulding. In this process, molten plastic or metal is injected into a mould cavity under high pressure. Once cooled, the material solidifies into the desired shape. This method is ideal for producing complex parts with high precision and is widely used for creating interior components, trim pieces, and exterior panels.
2. Blow Moulding
Blow moulding is used to produce hollow parts, such as fuel tanks and air ducts. In this process, a tube of molten material is inflated within a mould to form the part. Blow moulding is valued for its ability to produce lightweight, durable components with uniform wall thickness.
3. Compression Moulding
Compression moulding involves placing a preheated material into an open mould cavity. The mould is then closed, and pressure is applied to shape the material. This method is commonly used for producing rubber or composite parts and is known for its ability to create parts with strength and durability.
Materials Used in Automotive Moulding
1. Plastics
Plastics are among the commonly used materials in automotive moulding. They offer a range of properties, including flexibility, lightweight, and resistance to corrosion. Common plastics used in automotive moulding include polycarbonate, polypropylene, and ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene). Each type of plastic is chosen based on its suitability for specific components and performance requirements.
2. Metals
Metal moulding is used for parts that require high strength and durability. Common metals used include aluminium, steel, and magnesium alloys. Metal moulding is often employed in structural components, engine parts, and other high-stress areas of the vehicle.
3. Composites
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fibreglass, are used in automotive moulding to combine the benefits of various materials. Composites offer a balance of strength, lightweight, and resistance to environmental factors, making them suitable for high-performance and specialized components.




 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666