Design Supply Auto Bumper Mold Exporter Producer Wholesaler
The automotive industry is continuously evolving, and with it, the demand for efficient manufacturing processes is on the rise. Every component of a vehicle plays a vital role in its performance and safety, and the auto bumper is no exception. To meet the ever-increasing demand for bumper production, manufacturers rely on auto bumper molds. These molds are essential in streamlining the manufacturing process and ensuring consistent, high-quality production. In this article, we will explore the significance of auto bumper molds and how they contribute to the automotive manufacturing industry.
1. What is an auto bumper mold?
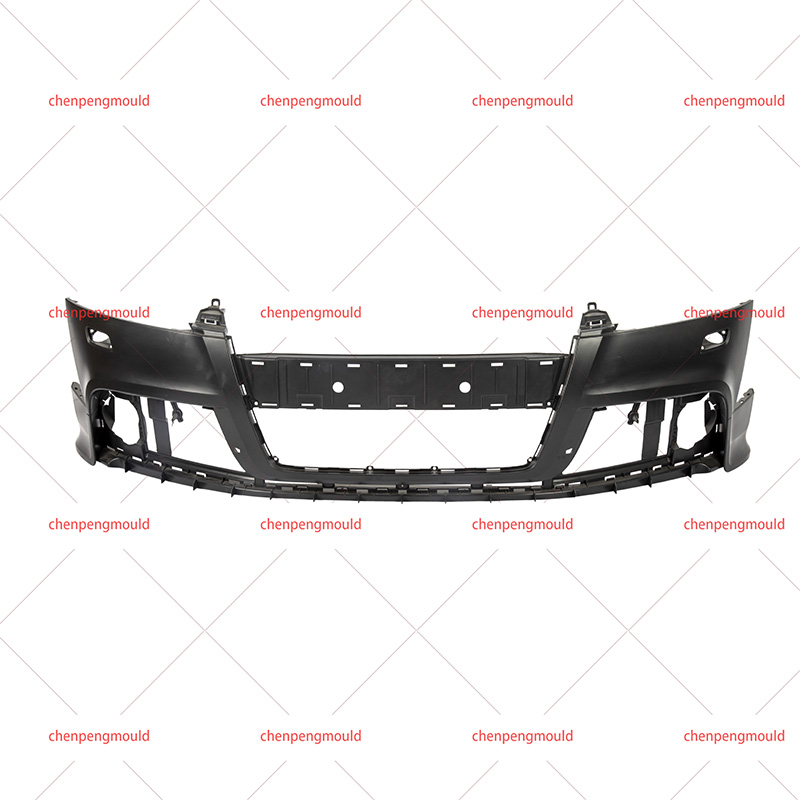
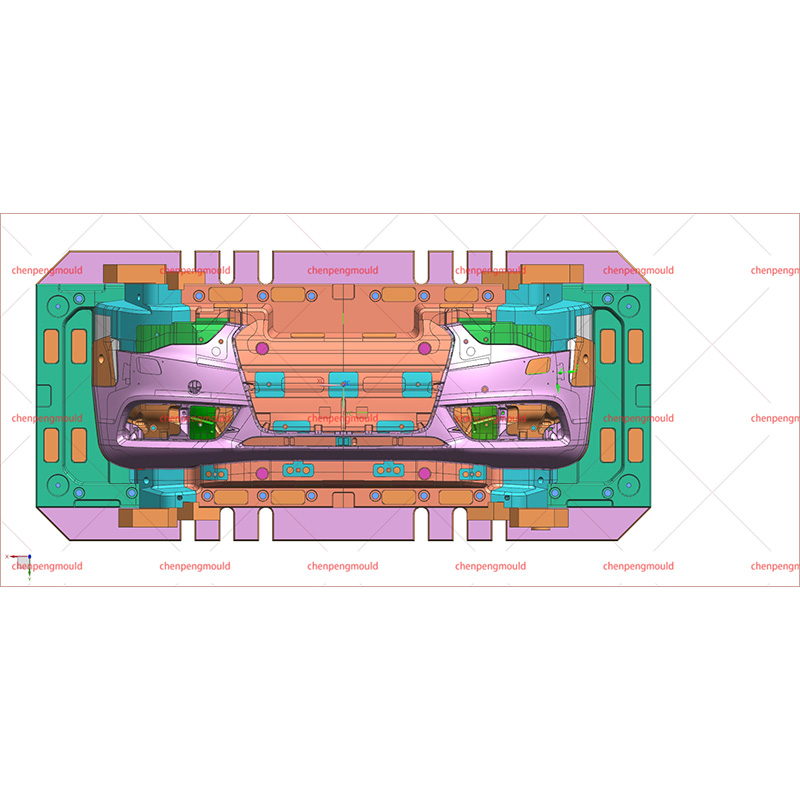
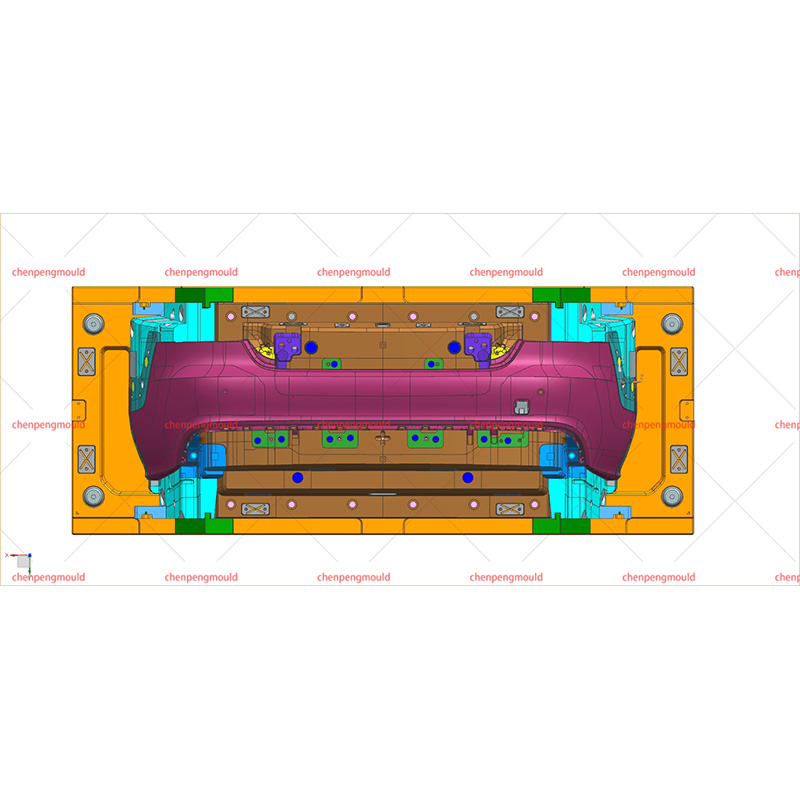
An auto bumper mold is a specialized tool used in the injection molding process to create bumpers for automobiles. The mold consists of two halves, an injection side, and a clamping side, that together form the desired shape of the bumper. These molds are typically made of high-quality steel or aluminum to withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved in the injection molding process.
2. How does the auto bumper molding process work?
The process of auto bumper molding involves several steps:
a. Mold Preparation: The auto bumper mold is inspected, cleaned, and prepared to ensure it is in good condition for the production run.
b. Material Selection: A suitable thermoplastic material, such as polypropylene or polyurethane, is chosen for the bumper's production. The material is then melted down and prepared for injection.
c. Injection: The melted material is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. This process allows the material to fill all the intricate details of the mold and form the desired shape of the bumper.
d. Cooling: Once the mold cavity is filled, the material is cooled rapidly to solidify and take the shape of the mold. Cooling can be accelerated through the use of cooling channels within the mold.
e. Ejection: After the material has solidified, the two halves of the mold are separated, and the finished bumper is ejected from the mold. The mold is then ready for the next production cycle.
3. What are the advantages of using auto bumper molds in automotive manufacturing?
Auto bumper molds offer several advantages that contribute to efficient automotive manufacturing processes:
a. Cost-Effective Production: By utilizing auto bumper molds, manufacturers can produce bumpers in large quantities, reducing the overall production costs per unit.
b. Time Efficiency: The injection molding process allows for quick production cycles. With the use of auto bumper molds, manufacturers can produce bumpers rapidly, minimizing production time and meeting customer demands.
c. Consistency and Quality: Auto bumper molds ensure consistent production by maintaining the same shape and dimensions for each bumper. This consistency translates into high-quality bumpers that uphold safety standards and meet customer expectations.
d. Design Flexibility: Auto bumper molds can be customized to incorporate various design features, such as grilles, fog light housing, or aerodynamic elements, to enhance the aesthetics and functionality of the bumper.
e. Durability and Longevity: Auto bumper molds are made from durable materials, allowing them to withstand the high pressures and temperatures of the injection molding process. This durability ensures the longevity of the molds, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
4. How are auto bumper molds manufactured?
The manufacturing of auto bumper molds is a complex and precise process. It involves several stages, including:
a. Design and Engineering: Skilled engineers and designers develop the mold design using computer-aided design (CAD) software. They consider factors such as bumper specifications, material characteristics, and production requirements.
b. Material Selection: High-quality steel or aluminum alloys are chosen based on their mechanical properties and heat resistance.
c. CNC Machining: The mold design is translated into instructions for precision machining equipment, like computer numerical control (CNC) machines. These machines carve out the mold cavities and other intricate details.
d. Heat Treatment: The mold components undergo heat treatment processes, such as hardening or tempering, to improve their strength, wear resistance, and durability.




 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666