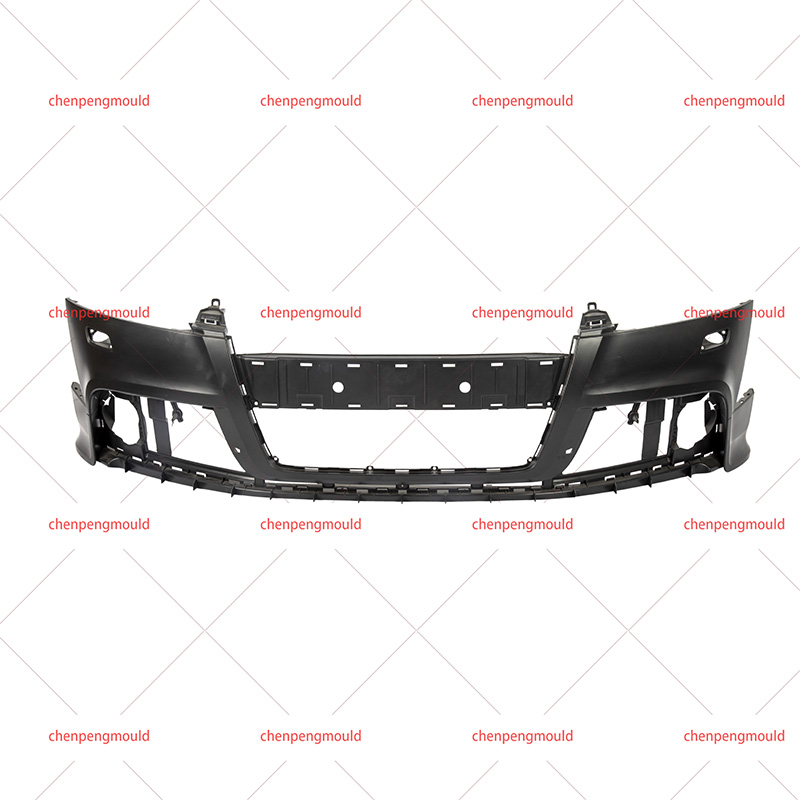
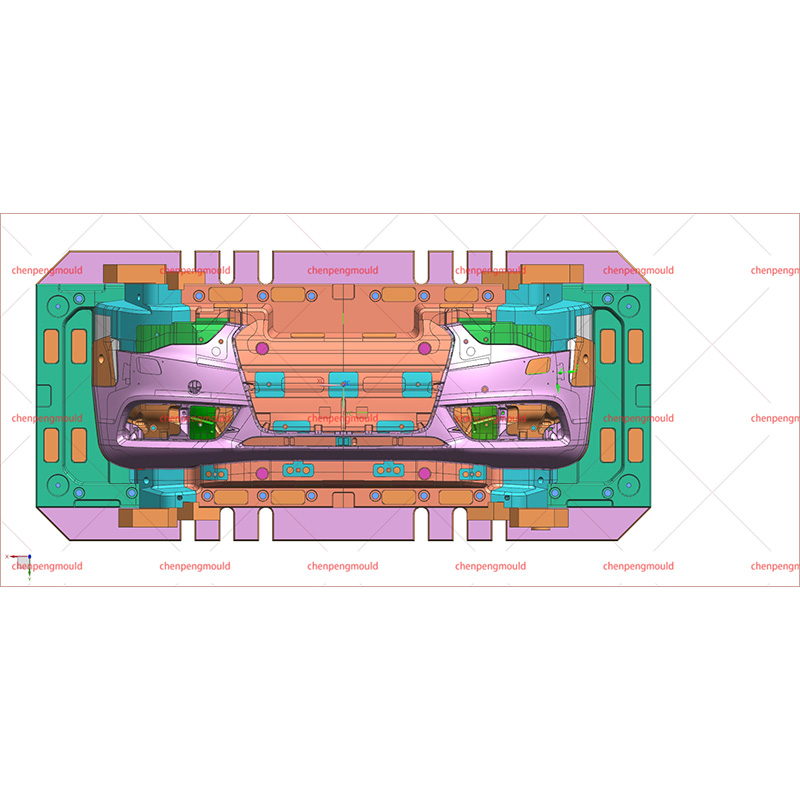
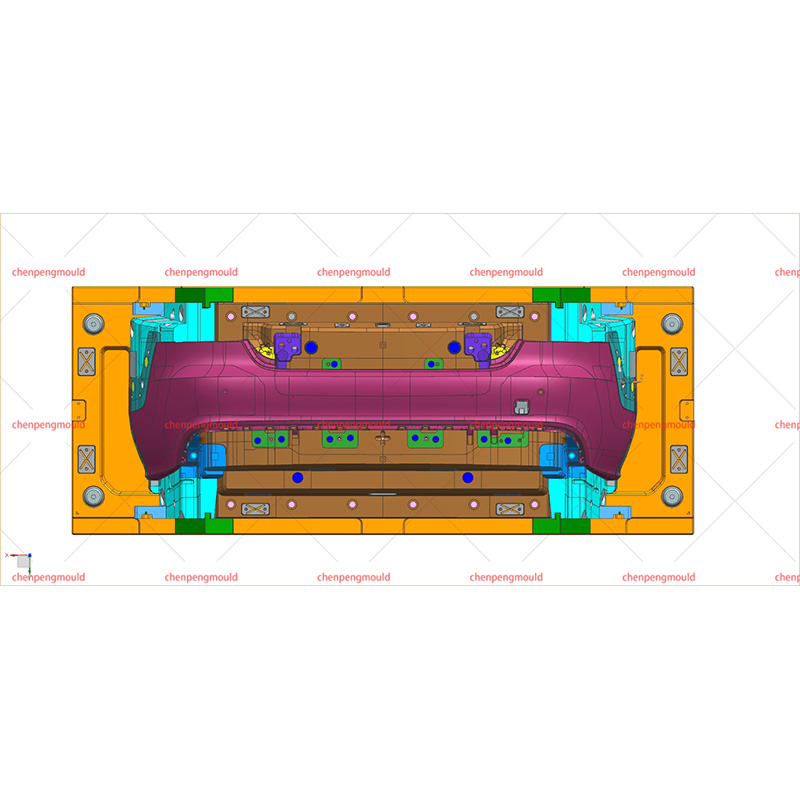
High Quality Front Bumper Molding Manufacturer Factory Supplier
The front bumper of a vehicle plays a critical role in ensuring safety, aesthetics, and overall functionality. It serves as the line of defense in a collision, absorbs impact forces, and contributes to the vehicle’s design identity. In the manufacturing process, front bumper molding is a key step, where materials are shaped into the desired bumper form through specialized molding techniques. The choice of front bumper molding is influenced by various factors such as the vehicle’s intended use, aesthetic preferences, regulatory requirements, and material properties.
This molding process allows manufacturers to produce bumpers with complex shapes, optimized strength-to-weight ratios, and integrated features like lights, sensors, and decorative elements. With modern molding techniques, bumpers can be tailored to meet the unique needs of different vehicle models, ensuring both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Key Factors in Choosing Front Bumper Molding
When selecting the right front bumper molding for a vehicle, several factors must be carefully considered. These include safety standards, the intended purpose of the vehicle, the material choice, and the design requirements. Let’s explore these factors in greater detail.
1. Safety Standards and Regulations
Safety is one of the important considerations when choosing front bumper molding. Bumpers are designed to absorb the impact energy of low-speed collisions, protecting the vehicle’s structure and occupants. Different countries and regions have specific regulations and standards that govern bumper performance, particularly when it comes to impact resistance, pedestrian safety, and vehicle compatibility.
For example, in the United States, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) sets guidelines for bumper height, strength, and impact resistance to damage to both the vehicle and pedestrians. Similarly, European regulations also require bumpers to meet specific safety criteria.
Manufacturers must ensure that the molding process and materials selected for the front bumper meet these regulatory standards. This often involves using impact-resistant materials, precise molding techniques, and incorporating features such as energy-absorbing zones into the bumper design.
2. Material Selection
The choice of material is a critical factor in the performance, cost, and durability of the front bumper. Various materials are available for bumper molding, each offering distinct advantages and limitations. The commonly used materials include thermoplastics such as polypropylene (PP), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), as well as composite materials like fiberglass-reinforced plastics (FRP).
Polypropylene (PP) is the widely used material for bumpers due to its balance of strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. It is lightweight, resistant to chemical damage, and can absorb impact forces without cracking or breaking. PP is often used in mass-market vehicles for its affordability and good overall performance.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is another popular material, known for its high impact resistance and rigidity. ABS is commonly used in higher-end vehicles where aesthetics and durability are important. It is more rigid than PP and offers better resistance to scratches and UV degradation.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) combine the flexibility of rubber with the durability of plastic, making them ideal for bumpers that need to absorb more impact without cracking. TPE materials also offer improved resistance to temperatures, making them suitable for use in different climates.
Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastics (FRP) are composite materials that offer a higher degree of strength and stiffness than traditional plastics. FRP bumpers are often used in vehicles that require extra strength, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, or high-performance cars.
The material chosen for front bumper molding must be carefully matched to the requirements of the vehicle, taking into account factors such as cost, impact resistance, weight, and environmental considerations.




 +86-18357617666
+86-18357617666